Overview of Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs)?
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) are prefabricated building materials used in construction. They consist of a core of rigid foam insulation sandwiched between two structural facings, typically oriented strand board (OSB) or plywood. This design provides excellent insulation, strength, and airtightness, making SIPs suitable for walls, roofs, and floors in residential and light commercial buildings.
Key Features of SIPs
Composition
Core Materials: Most commonly made from expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene or (GPS), graphite expanded polystyrene
Facing Materials: Most commonly include OSB, or magnesium oxide board.
Structural Benefits
Strength: SIPs have structural properties similar to steel I-beams, allowing them to handle significant loads.
Energy Efficiency: They provide continuous insulation, reducing thermal bridging and improving energy efficiency.
Advantages of Using SIPs
Speed of Construction: SIPs can reduce framing time by up to 55% compared to traditional wood framing.
Reduced Waste: Factory manufacturing minimizes on-site waste and allows for precise cutting.
Environmental Impact: SIPs contribute to lower energy use and greenhouse gas emissions throughout their lifecycle.
Considerations and Challenges
Moisture Control: Proper installation is crucial to prevent moisture issues, particularly at panel joints.
Fire Safety: SIPs require a fire-resistant thermal barrier, typically gypsum board, to meet building codes.
SIPs are a modern building solution that combines efficiency, strength, and sustainability, making them a desirable option for many construction projects.
-
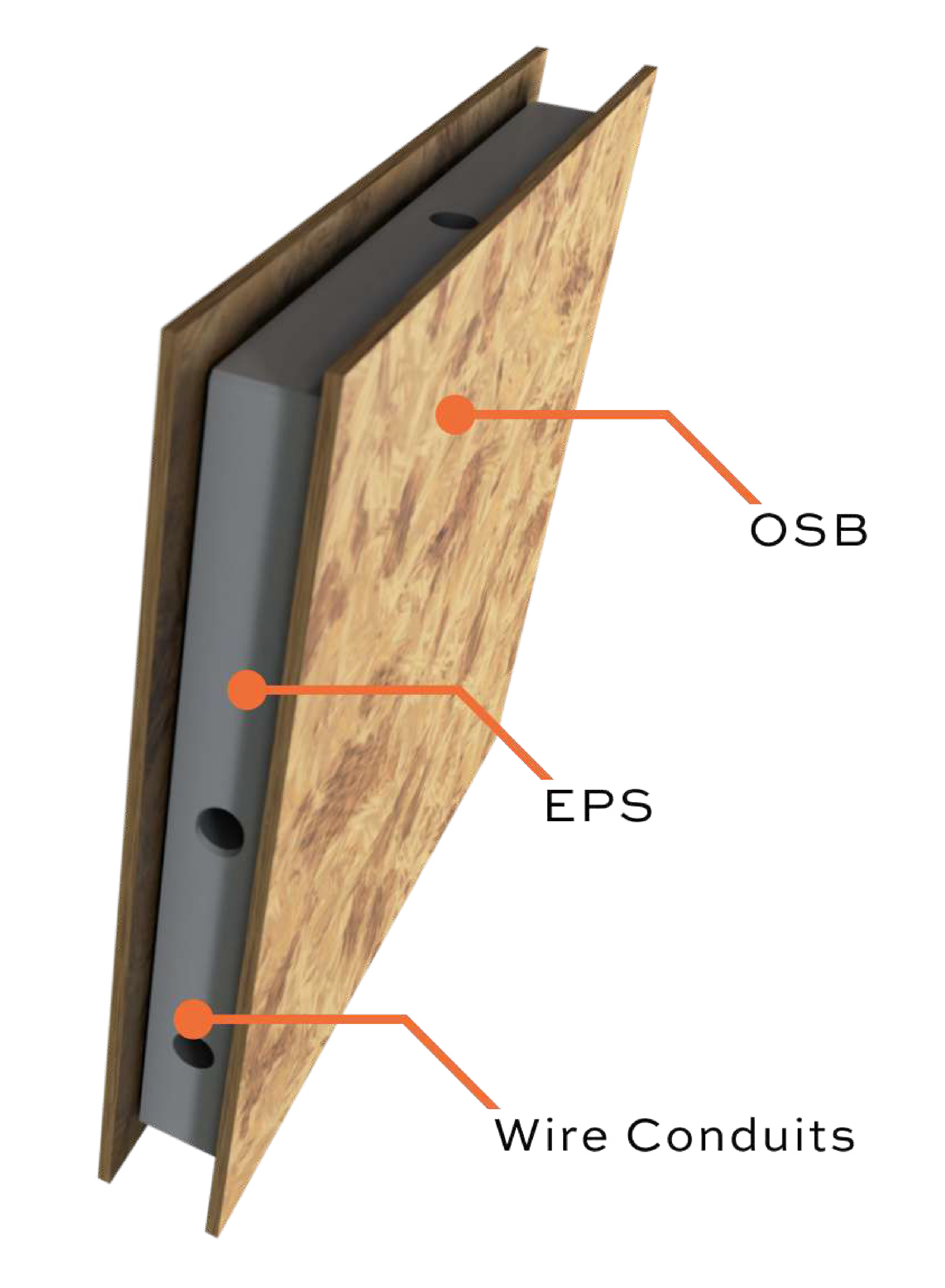
Simple to Build
-
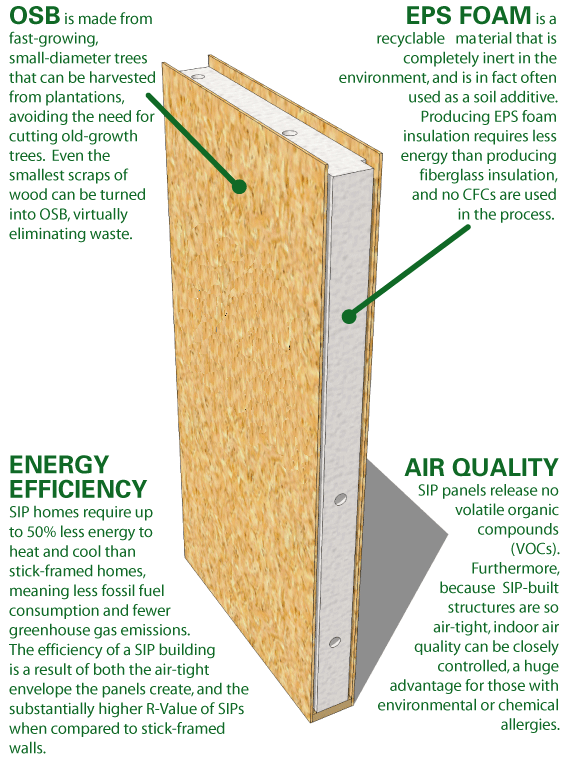
Benefits
-

Ready to Assemble

