Overview of Insulated Concrete Forms (ICF)
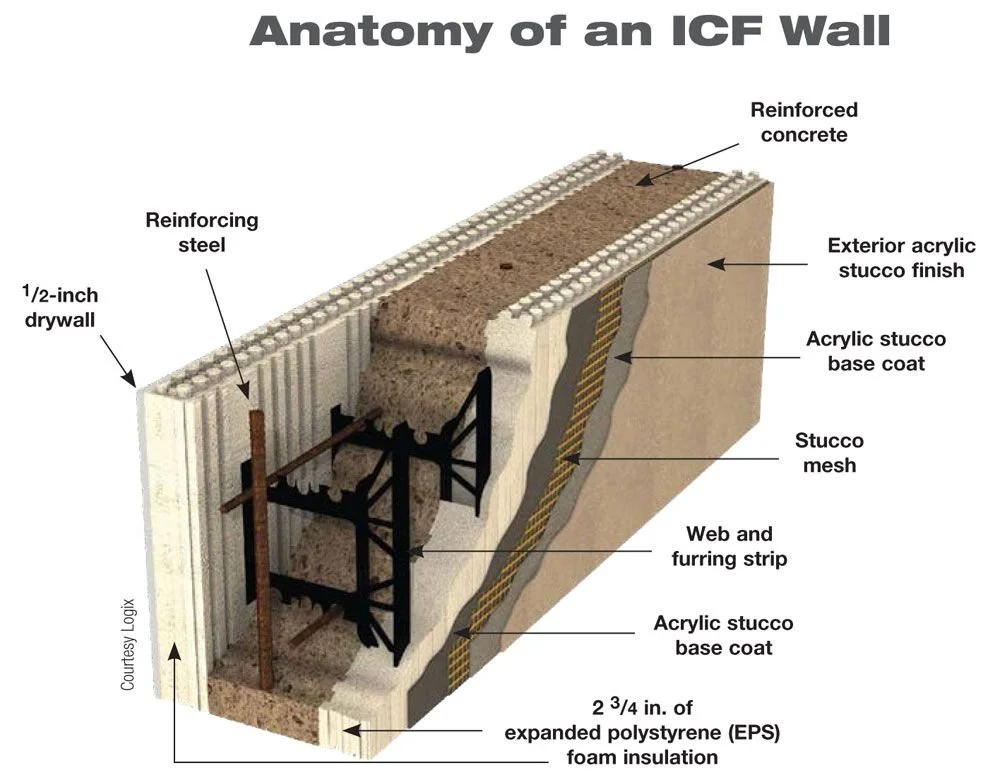
Insulated Concrete Forms (ICF) are a modern building system used to create walls and floors with integrated insulation.
They consist of blocks made from materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS) or cement-bonded wood fiber.
These blocks are stacked and filled with concrete, forming a strong and energy-efficient structure.
Construction Process
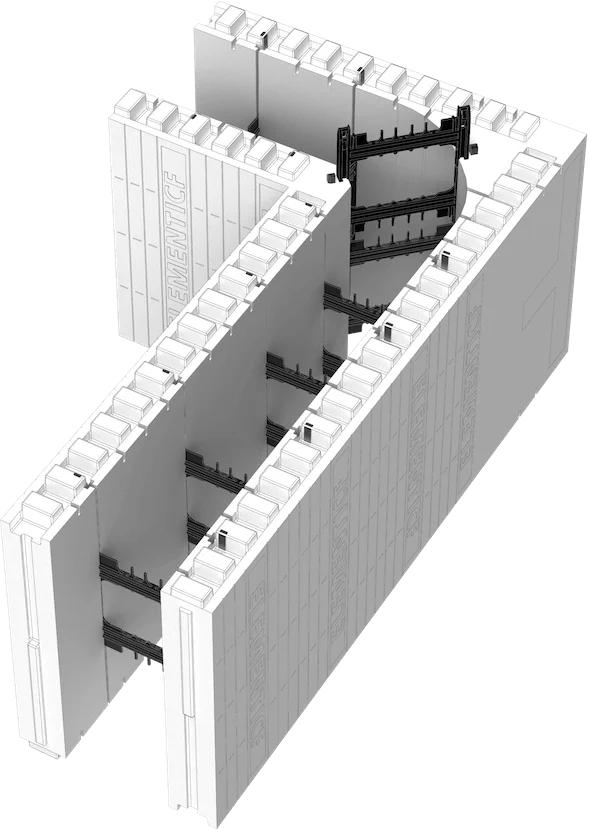
Interlocking Design: ICF blocks fit together like Lego bricks, allowing for easy assembly.
Concrete Filling: Once the blocks are in place, concrete is poured into the cavities, providing structural integrity.
Permanent Insulation: The forms remain in place after the concrete cures, offering continuous insulation on both sides of the wall.
Energy Efficiency
High R-Value: ICF walls typically have a better R-value compared to traditional wood-frame walls, enhancing thermal performance.
Air Sealing: ICF construction minimizes air leakage, contributing to lower energy costs over time.
Types of ICF Systems
Description
Flat Wall System Solid concrete wall with uniform thickness and insulation on both sides. This is the most common for residential use.
Waffle Grid System Concrete wall with a grid of reinforced concrete, providing strength and insulation.
Screen Grid System Similar to waffle grid but with more solid areas of insulation.
Advantages of ICF
Strength and Durability: ICF structures are robust and can withstand extreme weather conditions.
Noise Reduction: The insulation properties help in soundproofing the building.
Sustainability: ICFs can contribute to energy-efficient building practices, reducing the overall carbon footprint.
ICF construction is increasingly popular for both residential and commercial projects due to its efficiency and performance benefits.